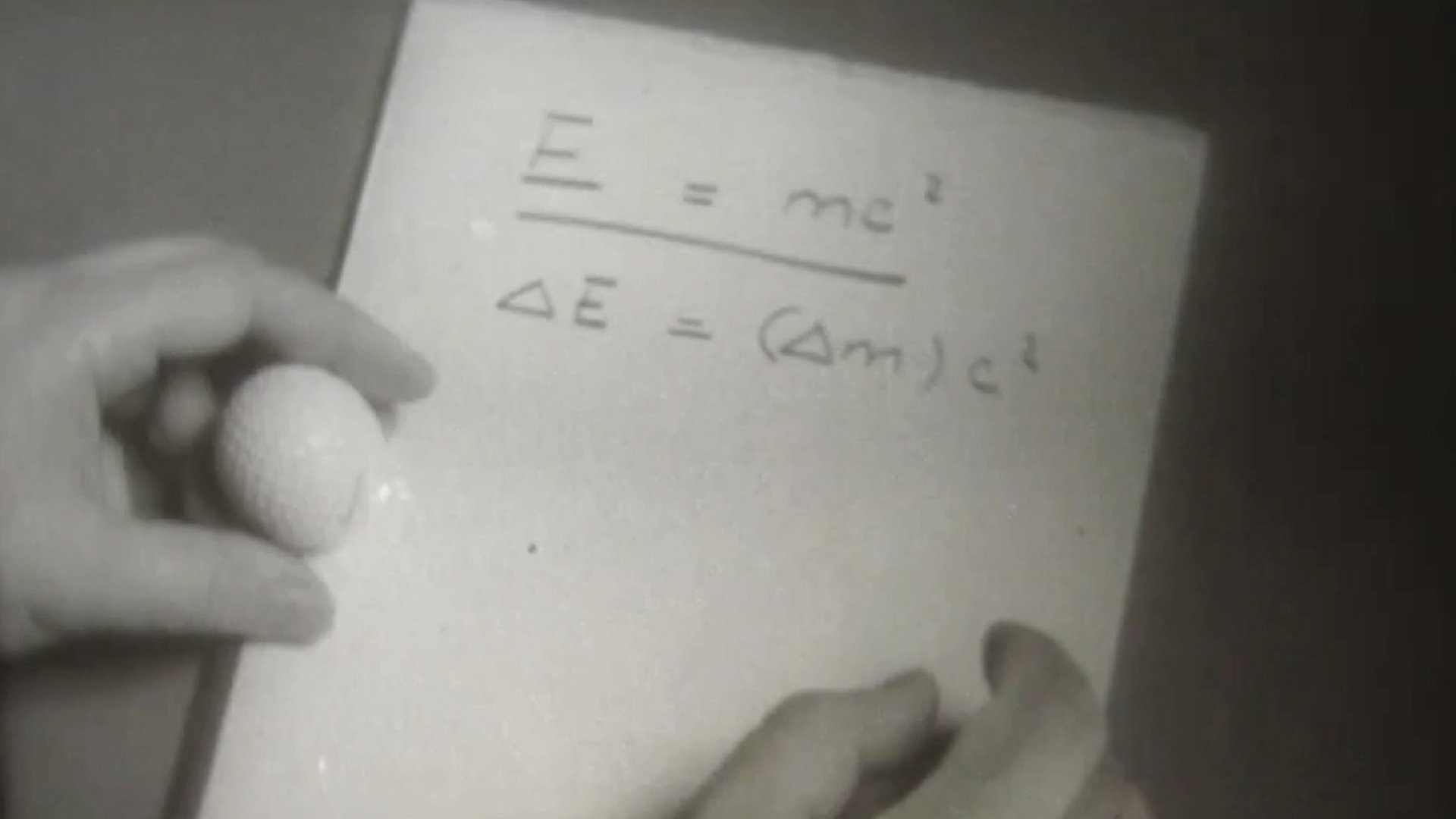Description
Electron–positron annihilation occurs when an electron (e−) and a positron (e+, the electron's antiparticle) collide. At low energies, the result of the collision is the annihilation of the electron and positron, and the creation of energetic photons: e− + e+ → γ + γ